The Dutch Tulip Bulb Market Bubble, also known as Tulip Mania, was a period in the 17th century when the value of tulip bulbs was driven to extremes by speculation. The period began in 1634 and ended in February 1637. In this article, we will delve deeper into the economic and social consequences of this mania, shedding light on the lessons learned from this iconic event.


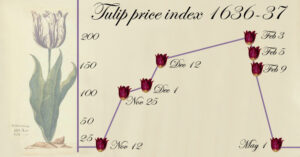
1. Economic Impact:
When the tulip market finally collapsed, the implications for the Dutch economy were significant. Let’s examine three key consequences:
a) Wealth Redistribution: The bubble’s collapse led to a redistribution of wealth as fortunes evaporated overnight. Investors who had put their life savings into tulip bulbs experienced devastating losses. Many became bankrupt, while others faced severe financial hardship. The redistribution of wealth impacted individual families and had a broader impact on the overall economic structure.
b) Trade Implications: The decline in tulip prices also impacted the Dutch economy on an international scale. Tulip exports had been a thriving industry, but the collapse led to a sharp decrease in demand, affecting not only tulip growers but also the numerous associated businesses such as florists, gardeners, and shipping companies. This decline in trade could be seen as a setback to the Dutch economic prosperity of the time.
c) Investor Confidence: The Dutch Tulip Mania shattered the trust and confidence of investors. The market crash exposed the pitfalls of speculative investments and made people wary of participating in future speculative bubbles. It took time for investors to regain trust and rebuild the foundation for economic stability.
2. Social Consequences:
The social impact of the Dutch Tulip Mania reverberated through various aspects of society. Let’s explore two prominent consequences:
a) Reputation of Tulip Bulbs: Prior to the mania, tulip bulbs were considered a luxury item and held social prestige. In the aftermath of the crash, tulips became a symbol of folly and irrationality. The burst bubble tarnished the reputation of tulip bulbs, and for a long time, they were seen as an impractical and unreliable investment.
b) Widespread Panic and Public Opinion: The ramifications of the tulip crash extended beyond the financial realm. The burst bubble created a sense of panic and despair among the general population. Many individuals lost their savings and assets, leading to social unrest. People began to question the irrational exuberance that drove the mania and the collective mentality that had allowed it to happen.
Conclusion:
The Dutch Tulip Mania serves as a cautionary tale, illustrating the potential consequences of speculative bubbles. The economic fallout highlighted the dangers of unregulated excesses and the importance of sound investment practices. Moreover, the social repercussions led to a shift in public sentiment and contributed to a more vigilant and prudent approach to financial matters.
By examining the economic and social consequences of the Dutch Tulip Mania, we can better comprehend the significance of this event in history. It serves as a reminder that the allure of quick wealth can lead to devastating outcomes when reason gives way to irrational exuberance.

